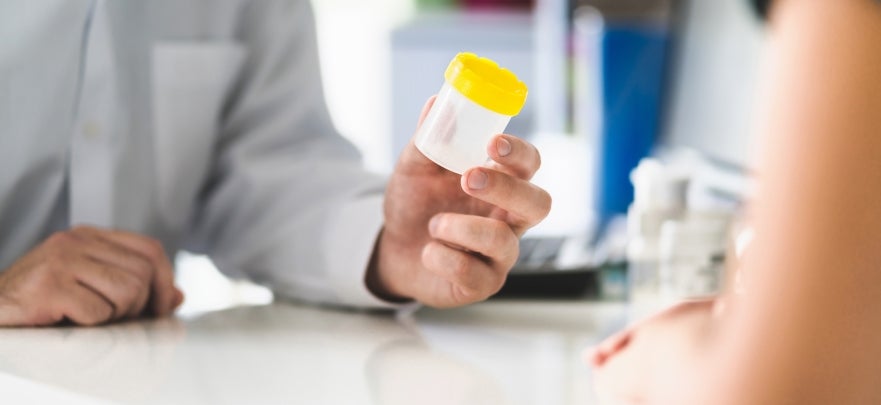
Diabetic Microalbumin Test
If you have high blood pressure or type 1 or type 2 diabetes, you’re at risk of developing kidney disease. A microalbumin test, which can detect early signs of kidney damage, is highly recommended.
Your kidneys filter waste from your blood and keep the healthy components, including proteins such as albumin. If your kidneys are damaged, proteins can leak through your kidneys and exit your body in your urine. Albumin is one of the first proteins to leak from damaged kidneys. A urine microalbumin test can detect very small levels of albumin in urine.
With early detection, a treatment program may prevent or delay more advanced kidney disease.
How to Prepare for the Test
Taking the urine test doesn’t require special preparation. You can eat and drink as you normally would before the test. Depending on what your doctor recommends, a random sample may suffice, or a 24-hour cycle of urine collection may be needed.
Urine may be collected several ways:
-
24-hour urine test. Your doctor may ask you to collect all of your urine in a special container over 24 hours and submit it for analysis.
-
Timed urine test. Your doctor may ask you to provide a urine sample first thing in the morning or after four hours of not urinating.
-
Random urine test. A random urine test can be taken at any time. But to improve the accuracy of the results, it's often combined with a urine test for creatinine—a waste product usually filtered by the kidneys.
Results of the microalbumin test are measured as milligrams (mg) of protein leakage over 24 hours. Generally:
-
Less than 30 mg is normal
-
Thirty to 300 mg may indicate early kidney disease (microalbuminuria)
-
More than 300 mg indicates more advanced kidney disease (macroalbuminuria)
Discuss your test result and what it means for your health with your doctor. If your urinary microalbumin level is higher than normal, your doctor may recommend repeating the test.
Several factors can cause higher than expected urinary microalbumin results, such as:
-
Blood in your urine
-
Some medications
-
Fever
-
Recent vigorous exercise
-
Urinary tract infection
-
Other kidney diseases